This document describes the protocol used in this module.
Implementing a protocol for a command line interface is not easy. One has to know what a protocol and a state machine is and how they work. Please see the following modules for more information:
Refer to Module 5.3.3 for an implementation example with a Visual Studio and a Code::Blocks solution.
- Protocol Definition
- Start Condition: O, F, B
- Stop Condition: space
- Message Format: 'COMMAND''ARGUMENT''TERMINAL' or 'COMMAND''ARGUMENT1''ARGUMENT2''TERMINAL'
- O num - Turn LED num on.
- F num - Turn LED num off.
- B num1 num2 - Let LED num1 blink num2 times.
- Protocol Implementation
- The protocol is implemented by the following finite state machine:
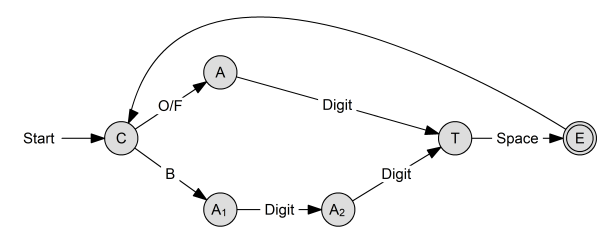
The description of the states is:
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| C | Parse command. |
| A | Parse argument of LED command. |
| A1 | Parse first argument of blink command. |
| A2 | Parse second argument of blink command. |
| T | Parse terminal character. |
| E | Execute command. |
The transitions are:
| State | Condition | Transition | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | token = O | A | Command is LED on. → Parse LED argument. |
| token = F | A | Command is LED off. → Parse LED argument. | |
| token = B | A1 | Command is blink. → Parse first blink argument. | |
| A | token = digit | T | LED argument parsed. → Parse terminal. |
| A1 | token = digit | A2 | First blink argument parsed. → Parse second blink argument. |
| A2 | token = digit | T | Second blink argument parsed. → Parse terminal. |
| T | token = space | E | Terminal parsed. → Execute. |
| E | - | C | Command executed. → Parse next command. |
Every parsing function gets the new token and returns the subsequent state. Some functions return extra information (command, argument) via a reference parameter. The basic workflow is as follows:
while (1)
{
switch (state) {
case CLI_STATE_GET_COMMAND:
token = new_token();
state = cli_parse_command(token, &command);
break;
case CLI_STATE_GET_ARGUMENT:
token = new_token();
state = cli_parse_argument(token, &argument);
break;
case CLI_STATE_GET_TERMINAL:
token = new_token();
state = cli_parse_terminal(token);
break;
case CLI_STATE_EXECUTE:
state = cli_execute(command, argument);
break;
}
}
